Classification and Prediction By Backpropagation
 | Rohit Kumar Mahadev |
Classification and prediction are two forms of data analysis that can be used to extract models describing data classes or to predict future trends. Classification predicts categorical(discrete, unordered) labels, prediction models continuous valued functions.
Classification:
- For loan application, bank manager can use a classifier to determine whether the applicant is "safe" or "risky".
- A spam filter can use a classifier to determine whether the email is "spam" or "not spam"
- A doctor can use a classifier to give "Treatment A" or "Treatment B" or "Treatment C" based on medical data of a patient.
Prediction:(Numeric Prediction)
- Marketing manager can predict the expenditures in dollars of a customer on a sale given their income and occupation.
- To predict housing price based on location and amenities.
There are many different types of algorithms available for classification and predictive modeling like k-nearest-neighbors, logistic regression and several other neural networks. Some algorithms are specifically designed for binary classification and others for multi class classification. Neural networks having high tolerance of noisy data as well as their ability to classify patterns with little knowledge of the relationship between attributes and classes can be used for both classification(to predict the class label of a given tuple) and prediction(to predict a continuous-valued output).
What is backpropagation? Backpropagation is a neural network learning algorithm which is a set of connected input/output units in which each connection has a weight associated to it.Backpropagation algorithm performs learning on multilayer feed-forward neural network which has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer as shown in the figure below.
- It is a feed-forward as none of the weights cycles back to an input unit or to an output unit of a previous layer.
- It is fully connected in that each unit provides input to each unit in the next forward layer.
- Given enough hidden units and enough training samples, this network topology can closely approximate any function.
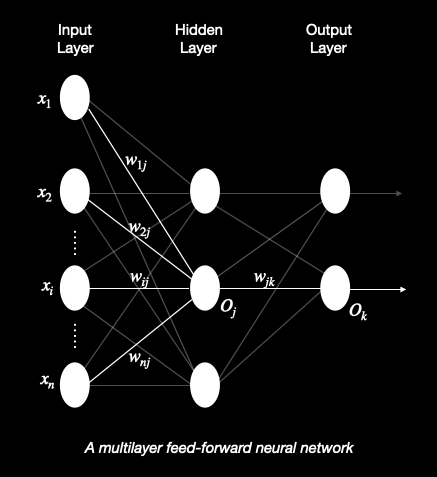
How does backpropagation works? Backpropagation learns by iteratively processing a dataset of training tuples, comparing the network's prediction for each tuple with the actual known target value. The target value may be the known class label of the training tuple(for classification problems) or a continuous value(for prediction). For each training tuple, weights are modified so as to minimize the mean squared error between the network's prediction and actual target value. These modifications are made in the backwards direction ie. from output layer through each hidden layer down to the first hidden layer(hence the name backpropagation)
Steps are described below:

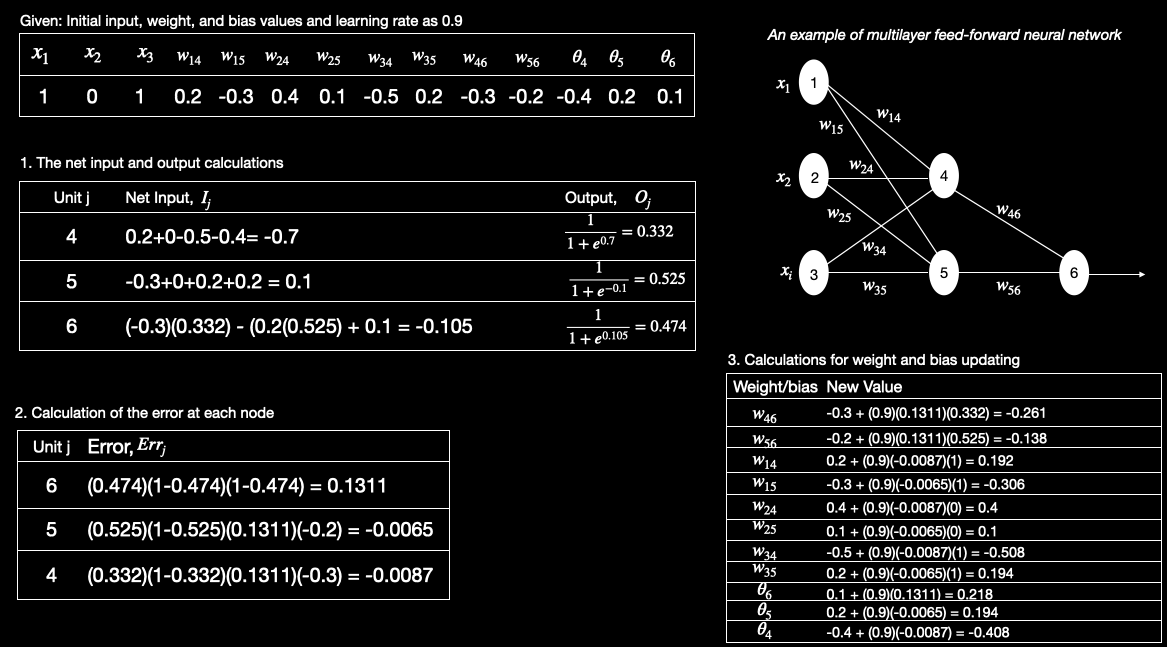
Example: Below example shows calculations for backpropagation of a multilayer feed-forward neural network with learning rate as 0.9. The initial weight and bias values of the network are given along with the first training tuple, X = (1,0,1), whose class label is 1.
- The tuple is fed into the network and the net input and output of each unit are computed(Table 1)
- The error of each unit is computed and propagated backward(Table 2)
- The weight and bias are updated based on the above algorithm(Table 3)
References:
- Data Mining by Jiawei Han and Micheline Kamber
- ML cheat sheet